Abnormal Fatigue in Athletes: Addressing RED-S
Carli Corpus, Dietetic Intern
Have you felt abnormal fatigue during practice, class, or even in social settings? Does your schedule prevent you from getting enough rest or fuel? For athletes, feeling tired after practice is normal. However, fatigue that lingers for days, or even months is not normal.
Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) is a common concern in athletics. It is known as an imbalance of energy intake to energy output. RED-S leaves you in a state of chronic low energy. This can also affect how you perform athletically.
RED-S contributes to a decrease in reproductive hormone levels in males and female. This increases your risk for bone injuries.
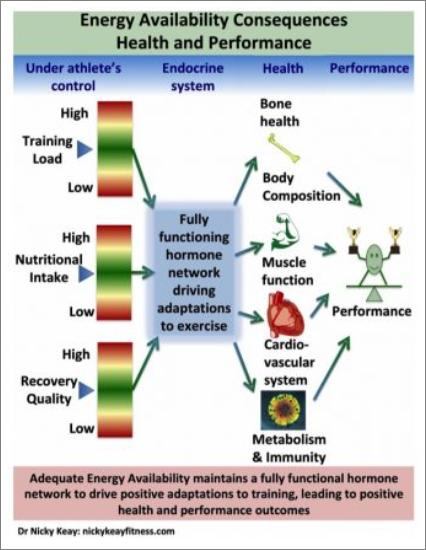
RED-S is more than just fatigue. Chronic low energy availability can cause deleterious consequences to your cardiovascular system, immune system, metabolism, as well as other hormones. Several factors increase you risk for RED-S:
- Not eating enough calories
- Lack of proper sleep
- Over-exercising
- A combination of these three factors
What Are the Signs of RED-S?
RED-S occurs in both men and women:
- For women, fatigue can be noticed when an athlete loses her monthly period. This is the body’s way of alerting you that energy is too low to have a menstrual cycle.
- For men, RED-S can be harder to notice. However, in addition to feeling abnormal fatigue, it can often be presented in a reoccurring injury cycle.
Beat RED-S and remain in the game for longer:
Fuel well, rest properly, and communicate concerns with others
who can help.

How Do I Address Abnormal Fatigue?
It is important to address the symptoms of RED-S sooner, not later.
Talk with your coach, athletic trainer, sports dietitian, or doctor about any symptoms you are experiencing. Work with them to develop a plan that will help you return to your usual training as a healthier athlete.
RED-S does not require you to end your sporting career. It is simply the body’s way of alerting you that it cannot function normally with low energy.
RED-S can present in other ways. You may notice a loss of motivation, heightened self-criticism, increased anxiety, and signs of depression. The excessive fatigue can thus impact daily life outside of athletics.
How Do I Prevent RED-S?
Awareness of RED-S is key in prevention. To increase your awareness about your risk for RED-S, take these 3 steps:
- Listen to your body. If you notice that your energy is low, seek help. This can help prevent RED-S related injuries.
- Be aware of your body’s hunger cues. Eating enough calories will also lower your risk for developing RED-S. To remain healthy, eat with the intention to fuel tired muscles and nourish body systems. Planning meals and snacks can help you stay fueled throughout the day.
- Take time to rest. Sleep well and exercise appropriately to help keep your energy levels balanced. Many athletes will admit they push themselves through practice, even when feeling excessive fatigue. Take time to check in with your body and note your fatigue level.

